MySQL Architecture Explained: A Technical Overview for Database Engineers
MySQL architecture is central to understanding how this relational database management system powers modern applications. MySQL is one of the most widely used relational database management systems (RDBMS) in modern application stacks. It powers everything from small web applications to large-scale data warehouses. Thanks to its support for high availability, transactions, indexing, and multi-user access, MySQL remains a core database technology across industries.
Moreover, MySQL is a key component of the LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP/Python/Perl). As a result, developers and database administrators rely on it for building scalable and reliable systems.
MySQL Architecture Overview
At its core, MySQL follows a client–server architecture. The MySQL server handles all database operations, while client applications connect to it to execute SQL queries.
Unlike PostgreSQL, which uses a process-per-connection model, MySQL uses a thread-based architecture. Each client connection creates a new thread within the server process. This approach allows MySQL to manage resources efficiently, especially in environments with many concurrent connections.
Key Layers of MySQL Architecture
MySQL architecture consists of three main layers, each responsible for a specific set of tasks.
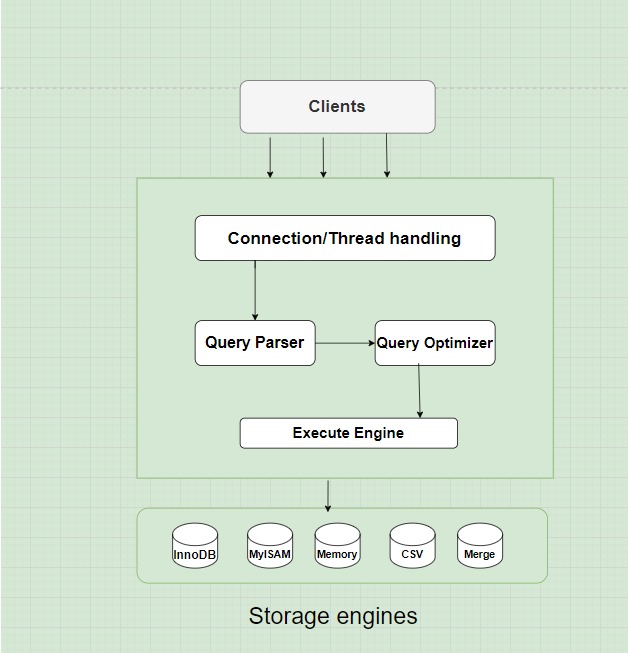
Application Layer (Client Layer)
The Application Layer is the entry point for all database requests. It includes:
-
-
MySQL client tools
-
Application connectors and APIs (JDBC, ODBC, Python, PHP, etc.)
-
Through this layer, applications send SQL queries and receive results from the MySQL server.
Logical Layer (SQL Processing Layer)
The Logical Layer acts as the brain of MySQL. It manages query parsing, optimization, execution, transactions, and recovery. Several critical components operate here.
Query Processing Components
MySQL processes SQL queries in a structured flow that ensures correctness and performance.
SQL Parser
First, the SQL parser validates query syntax and structure. It breaks the query into tokens and prepares it for optimization.
Query Cache (Removed in MySQL 8.0)
Earlier MySQL versions used a query cache to store result sets. However, MySQL 8.0 removed this feature because frequent table updates caused cache invalidation and performance degradation.
Query Optimizer
Next, the query optimizer evaluates multiple execution plans. It then selects the most efficient plan based on table statistics, indexes, and cost estimates.
Storage Engine Layer
The Storage Engine Layer defines how MySQL stores and retrieves data on disk. MySQL supports multiple storage engines, which gives it flexibility across different workloads.
InnoDB Storage Engine
InnoDB is the default and most widely used storage engine. It supports:
-
-
-
-
ACID-compliant transactions
-
Row-level locking
-
Foreign key constraints
-
-
-
Because of these features, InnoDB is ideal for transactional and high-concurrency systems.
MyISAM Storage Engine
MyISAM focuses on fast read performance and has a simpler design. However, it does not support transactions or foreign keys. Therefore, it is best suited for read-heavy workloads where strict consistency is not required.
Why MySQL Architecture Matters for Performance and Scalability
Understanding MySQL architecture helps database teams:
-
-
Design efficient schemas and queries
-
Choose the right storage engine
-
Tune performance for high-concurrency workloads
-
Scale applications more effectively
-
In addition, architectural knowledge allows teams to troubleshoot performance issues faster and plan capacity more accurately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MySQL’s layered and modular architecture makes it a powerful, flexible, and scalable database platform. Its client–server model, thread-based connection handling, and pluggable storage engines support a wide range of application needs. By understanding MySQL internals, engineers can unlock better performance, reliability, and long-term scalability for their database-driven applications.
Follow our more blog for mysql new features and for increasing performance and database adminstrator services reach out to us https://bynatree.com/contact/.







