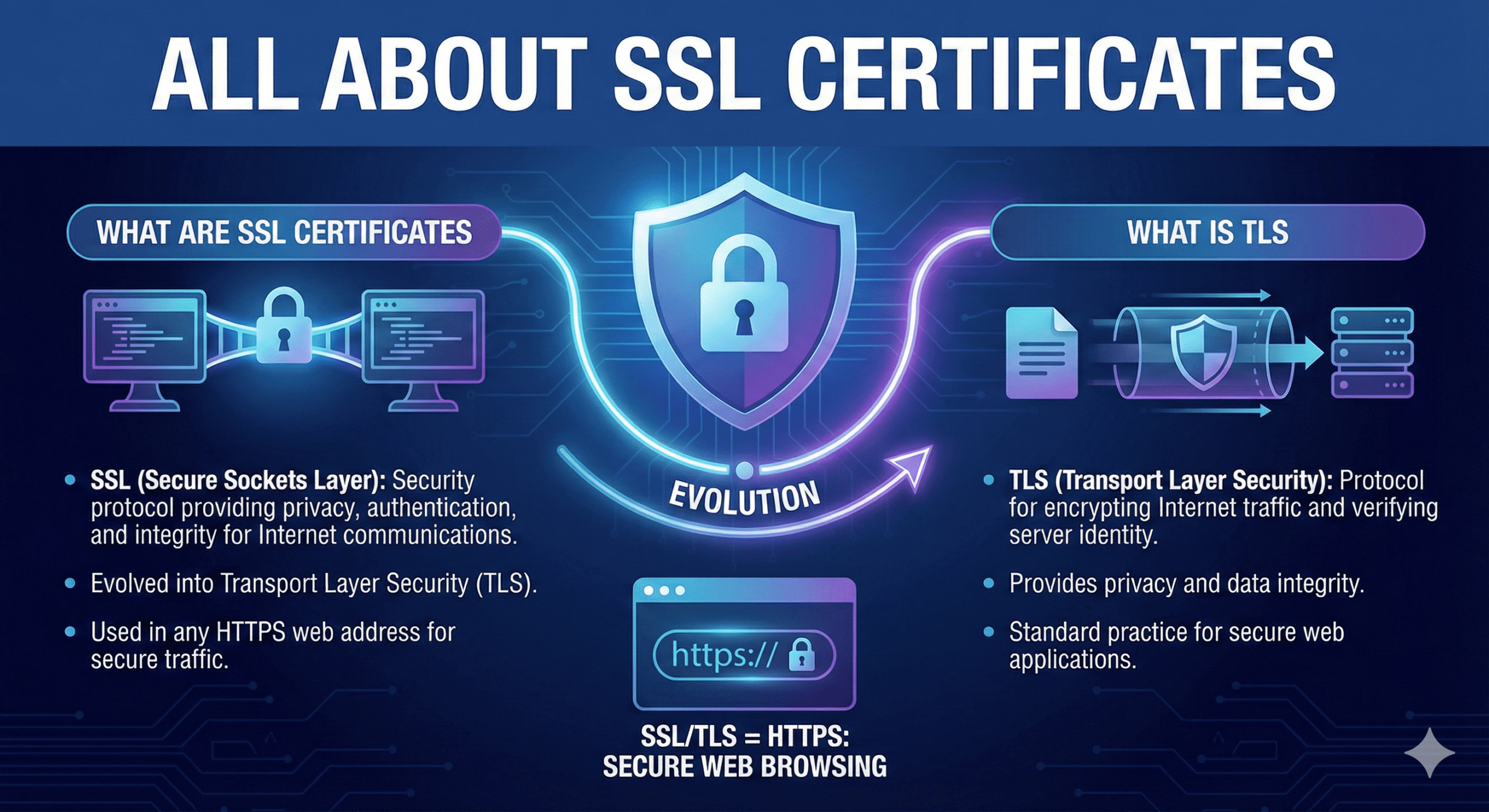
What are SSL certificates:-
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a cryptographic security protocol designed to provide data privacy, authentication, and integrity for internet communications. Over time, SSL evolved into Transport Layer Security (TLS), which is now the industry standard.
Although the term SSL certificate is still widely used, modern websites actually use TLS encryption to secure internet traffic and verify server identity.
What is TLS:-
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a security protocol that provides privacy and data integrity for Internet communications. Implementing TLS is a standard practice for building secure web applications.
Key Features of SSL certificates:-
SSL certificates provide multiple security mechanisms that work together to protect data:
Encryption – Converts data into unreadable ciphertext
Fragmentation – Breaks data into smaller packets
Confidentiality – Prevents unauthorized access
Integrity – Ensures data is not altered in transit
Server Authentication – Verifies website identity
Client Authentication – Verifies client identity (optional)
Types of SSL certificates:-
There are several types of SSL certificates. One certificate can apply to a single website or several websites, depending on the types:
- Single-Domain SSL Certificate – Protects one specific domain only.
Wildcard SSL Certificate – Protects one domain and all its subdomains (e.g., blog.example.com).
Multi-Domain SSL Certificate (SAN) – Protects multiple unrelated domains under one certificate.
SSL certificates also come with different validation levels. A validation level is like a background check, and the level changes depending on the thoroughness of the check.
- Domain Validation (DV) – Confirms domain ownership; fastest and least expensive.
Organization Validation (OV) – Verifies business identity; higher user trust.
Extended Validation (EV) – Requires full background verification; highest trust level.
How does an SSL certificate work:-
- It’s to provide a high degree of security; SSL encrypts data that is transmitted across the web. This means that anyone who tries to intercept this data will only see a garbled mix of characters that is nearly impossible to decrypt.
- SSL initiates an authentication process called a handshake between two communicating devices to ensure that both devices are really who they claim to be.
- SSL also digitally signs data in order to provide data integrity, verifying that the data has not been tampered with before the intended recipient.
Managing Certificates (OpenSSL Commands)
In a professional environment, you don’t just “get” a certificate; you generate and manage it using tools like OpenSSL. Here are the essential commands for each stage:
Step 1: Generate a Private Key and CSR
Before getting a certificate, Generate a Private Key and Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
- Command:
| 1 | openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout yourdomain.key -out yourdomain.csr |
- Purpose: Creates a private key and CSR file to submit to a Certificate Authority (CA).
Step 2: Check the CSR
Before sending the CSR to a provider ( Encrypt), you should verify the information in correct.
- Command:
| 1 | openssl req -text -noout -verify -in yourdomain.csr |
- Purpose: Ensure the domain name and organization information are accurate.
Step 3: Verify the issued Certificate
Once the CA sends you the .crt file, you can inspect its details expiration date and issuer.
- Command:
| 1 | openssl x509 -in yourdomain.crt -text -noout |
Purpose: Checks the validity and not after (expiry) date.
Step 4: Check if key and Certificate Match
A common error is trying to install a certificate with the wrong private key.
- Command to check key:
| 1 | openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in yourdomain.key | openssl md5 |
- Command to check Cert:
| 1 | openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in yourdomain.key | openssl md5 |
Conclusion:
SSL certificates are no longer optional—they are mandatory for modern websites, improving security, SEO rankings, and user trust.
With free options like Let’s Encrypt readily available, there’s no reason to delay. Implementing SSL builds trust, improves search ranking, and meets the security expectations of modern internet users. In today’s digital world, they padlock icon isn’t just a nice feature – it’s a necessity.
Please follow our other blogs High Availability PostgreSQL 16.11 Cluster with repmgr 5.5 on CentOS Stream 10